
What is Analytics for ecommerce?
Analytics for ecommerce are a great way to study user behavior in an online sales channel, and apply improvements based on that data.
When it comes to improving online store conversions, it is essential to have in-depth knowledge about:
- Who the buyers are
- How they reach the store website
- What interests them on the product pages
- How much time they spend on them
- How many of them end up making a purchase
We have previously discussed the effectiveness of heat map tools and eye-tracking software to obtain visual reports on visitors to your website. If you’re interested, you can learn about them in detail here, but right now we are going to look at another system that offers you much more in-depth data on how your online business is performing.
→ You may also be interested in: How to appear in Google’s top results
There are dozens of ecommerce analytics programs out there for you to choose from, but the most well known and versatile is Google Analytics for Ecommerce. The fact that it’s free has also contributed to its popularity among small and medium-sized companies.
If you prefer to see what else is out there or you’re not keen on Google’s controls, you can check out other ecommerce analytics tools such as Klipfolio, Tableau, or Microsoft’s PowerBI, which is a more professional and complex business solution.
Oh, and before you explore all the possibilities of ecommerce analytics, remember that to harness this user behavior data, your website must comply with GDPR regulations. Make sure to have cookies and required notifications in place so you can collect data with the consent of your customers.
And now that’s covered, let’s get analyzing!
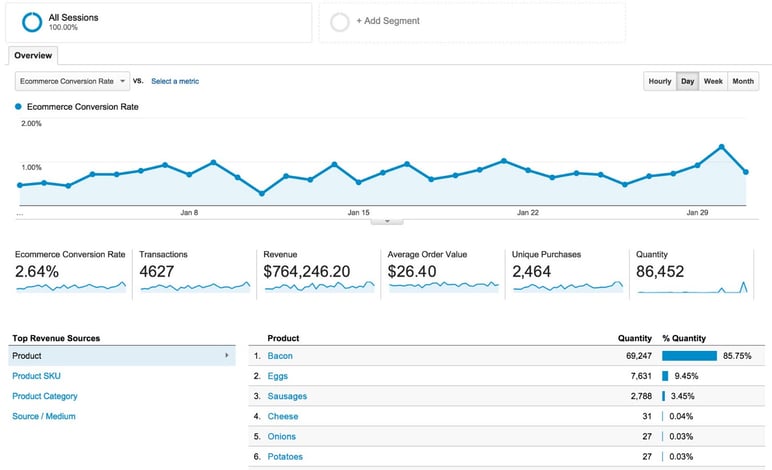
Key metrics for ecommerce: Everything you can improve with Analytics
Buyer persona
In many cases, improving a product means improving your idea of who wants to buy it.
Analytics in ecommerce allow you to study visit and purchase behaviors in depth according to demographic groups (e.g., gender and age), different geographical regions, and types of devices used to search (e.g., computer, mobile, etc.).
Analytics data are also helpful for finding out about the behavior of your buyers and deriving patterns of what first-time visitors, repeat visitors, and customers leaving the store typically do.
→ Learn more: Product Experience: The key to getting conversions
Marketing results
Launching marketing campaigns and actions involves keeping a constant watch on your results. Analytics applied to ecommerce reveal how your traffic and leads are growing, where they are originating from, and how each channel is performing.
The most critical areas you should analyze in ecommerce marketing are:
- Ads: Review the performance and cost of your Google ad campaigns along with click-through, bounce, and conversion rates.
- SEO: Compare which keywords you are using, and which ones are being searched the most.
- Website and app load time: Check if something is slowing down the speed of your pages.
- Content: Find out which parts of a page receive more clicks, which sections are being read the most, what the average time spent on a page is, how many views each page has, and more.
- Internal searches: Determine what terms your visitors are searching for, what the most visited categories are, and what products are being ignored.
- Payment process: A critical step in ecommerce that enables you to analyze where in the payment process users spend the most time and at which stage they most frequently exit before completing the transaction.
→ More tips: How to improve the speed of your ecommerce website
Product optimization
Many analytics focus on search engine positioning and the performance of advertising campaigns, marketing actions, and sales channels.
But we can’t forget that the main driver of all this activity is still the product. That’s why analytics also allow you to study what products in your catalog or sales channels are the most popular, which ones are not performing and could create inventory problems, and how many individual sales each product generates.
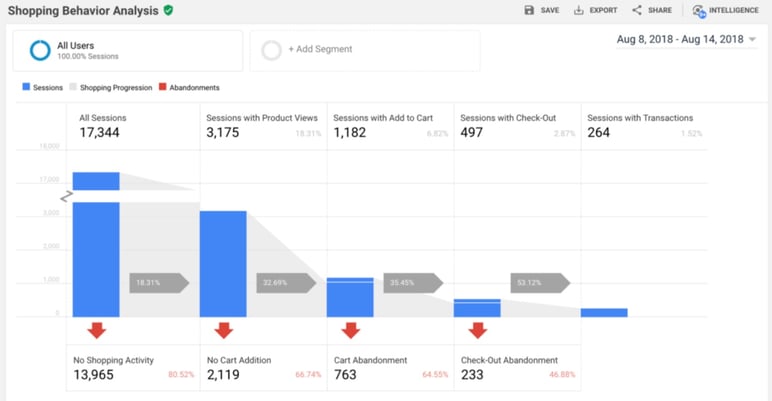
Analyze your business figures: How Google Analytics for ecommerce works
As we’ve seen, Google Analytics is the star of analysis tools for ecommerce. Its popularity has especially risen since the company began offering specific tools for ecommerce businesses and their products.
As in other areas of analysis, Google Analytics for Ecommerce works through a process of formulating objectives, implementing tools, and collecting data.
Once this framework is created, you can start analyzing the results in dashboards that show progress over time, within the periods you indicate and on the aspects that you decide are most important for assessing your business.
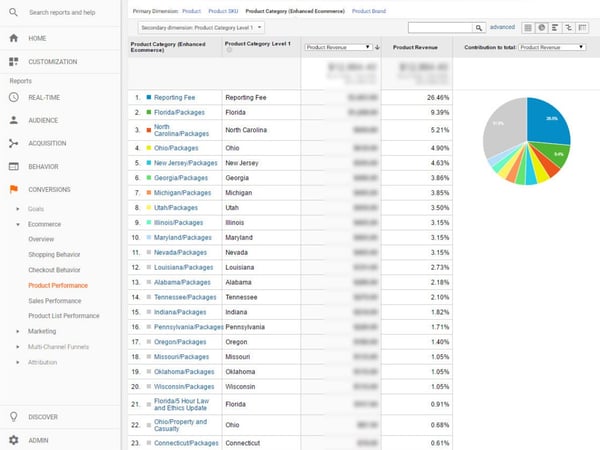
To use Google Analytics, you simply need a Google account to link it to. Once you sign up for Google Analytics you will have access to a wide array of benefits:
- Intuitive and easy-to-use.
- Customizable settings (comes with API, if you have more advanced knowledge).
- A broad community of support and forums with resources as well as frequently asked questions and common issues.
- And, best of all, free of charge.
→ To analytics and beyond! 100 tools to become the best marketing director
How to configure Analytics for ecommerce
Analysis objectives
The most important step, even before creating an account, is to be clear about what your business analysis plan will be.
Defining your objectives will allow you to configure Google Analytics more easily, since you will know what aspects you want to analyze within which time frames as well as what results you hope to achieve after implementing changes and improvements.
Your KPIs are those ecommerce metrics that you are most interested in analyzing. They can be about the number of visits to your channels, conversion rates, average costs, the cost of acquiring new customers, or the customer lifetime value.
You don’t want to know everything, since this would require a huge team to study literally all the metrics at the same time. Always prioritize your metrics, adjusting them as you go.
→ Pick your metrics: What KPIs are there to analyze your ecommerce business?
A few years ago, Google added the Enhanced Ecommerce option that includes many more opportunities for analysis.
These are the most relevant Enhanced Ecommerce features, but we recommend that you do a preliminary evaluation to see which ones would be most useful for your ecommerce business as it stands today:
- Campaign tracking: impression data, clicks, and CTRs.
- Use of promotional coupons.
- Comparison between numbers of successful orders and returns.
- Segmentation variables of the payment process by payment method (e.g. credit card, PayPal, Stripe, etc.).
- Analysis variables by brand, product views, frequency with which each product is added to the shopping cart, and more.
Google Analytics installation
Once you have created your Google Analytics account, there are a few, somewhat complex, steps to take before you can get up and running. Let's start with the simplest step:
- Add your website to the account.
- Edit access, read, collaboration, and edit permissions if multiple individuals are going to be accessing the account.
- Install the tracking code on your website.
This code will send information from your website to Google Analytics and there are several ways of installing it:
- Manually, by adding it to your website code.
- Automatically, by using Google Tag Manager, which allows you to select more than one tracker simultaneously.
- Via a specialized plugin.
In your tracking code, you can select different types of trackers, which is why it’s truly to your advantage to develop an analysis plan from the start:
- Pages you want to analyze
- Payment process
- Apps and downloadable documents
- On-page events you want to analyze: button clicks or CTAs, video playbacks, downloads, forms, etc.
- One or more domains
→ Don’t stop there! More ecommerce tools to make your life easier
Advanced features of Google Analytics
So far, we have looked at the basic steps for implementing Google Analytics for ecommerce quickly and effectively.
If you don’t have much experience studying this type of data or your business is not very large, it may be enough for you to analyze the basic metrics and implement gradual improvements.
But if you need more complex analyses or have a team prepared to monitor the key variables of your ecommerce business on a daily basis, then you have many more options moving forward:
- Review reports (primary or by demographic).
- Run tests, develop plans by objective, and assign a set duration.
- Compare your website with those of competitors in the same sector through benchmarking.
- Create analysis filters that are more customized.
You can also link your Google Analytics for Ecommerce account with other Google products:
- Google Data Studio, which is very useful for creating dashboards with automatic reports of the KPIs that you are most interested in reviewing frequently
- Google Ads, AdSense, and Ad Exchange for analyzing the performance of your campaigns
- Google Optimize and Tag Manager
- Google Search Console
- Google Cloud BigQuery
- Display & Video 360
- Search Ads 360
- Google Play
Apart from being simple enough to install, you can begin reviewing results from Google Analytics quite quickly. Just like in Ads, sometimes it takes a day for the data to be fully updated. For this reason, Google Analytics may be a more limited tool for large businesses that require real-time reactions.
→ Improve your content: Essential SEO techniques for ecommerce
Analytics data interpretation
A number-crunching dashboard is a wonder to behold, but now it’s time to interpret the data!
Luckily, Google Analytics results are displayed in a very visual and easy-to-understand way.
With the data you regularly receive on your ecommerce activity, you’ll be able to draw conclusions and make changes regarding the following:
- Technical problems on your website, such as pages that fail to load, broken URLs, problems with processing payments, and slow speed.
- Improvements that can be applied on your website by demographic group or product.
- Personalization of your website according to the profile of the user that enters it (based on the behavioral data that Google Analytics identifies as most frequent).
- Product suggestions adapted to each buyer (upselling and cross-selling) to encourage an increase in average spending.
- Online ad performance and email marketing campaigns.
- Identification of users who abandon the purchase process, so you can re-engage them as future customers.
Conclusion
What could be better than a simple and free tool to boost your business? Analytics can be intimidating at first, with its dashboards full of graphs and figures.
Yet Google Analytics is a very accessible way to become familiar with analytics for ecommerce and will enable you to convert data that’s already available in your online store into new sales opportunities.
Get to know your visitors and buyers better while improving your products and how they are presented to increase interest. Change everything that can be improved on your website and app to continue growing in a marketplace where success is not about sprinting forward, but rather taking the time to analyze.





.png?width=520&name=Blog%20Partner%20(3).png)

.png?width=520&name=Blog%20Partner%20(1).png)
