What is robotics in logistics?
One of the trends that is steadily advancing but less talked about is the application of robotics and artificial intelligence to logistics and transport. The business change that this application brings with it is quite large, with positive consequences for some and negative consequences for others. Before this scenario becomes more mainstream, companies and manufacturers have to become familiar with robotics and machine learning.
Robotics applied to industrial distribution means using robots and machinery with smart systems to automate tasks like organization, transfers, delivery, and product retrieval in a warehouse.
The different between traditional machinery and industrial robots is that the latter are associated with artificial intelligence systems that allow them to handle more complex variables and react quickly and independently by means of algorithms.
That is to say, compared with a robotic arm in a conventional production line, a smart logistics robot can learn new tasks and execute them to cover things that needed human assistance up until now. Industrial robots also help to support manual work, streamlining processes.
→ Related: logistics as the new value in ecommerce
The difficulties of artificial intelligence in the warehouse
Obviously, the shift of artificial intelligence applied to logistics and distribution is necessary; thus, it is important for the industry and its players to work on three fronts:
- Promoting knowledge about artificial intelligence robotics.
- Working on new standards to face costs and changes.
- Promoting the acquisition of new technologies amongst logistics companies to accelerate adaptation to the future.

It is true that robots that work in logistics with algorithms based on artificial intelligence are still expensive and can cost around €100,000 per unit. The cost per hour of a worker continues to be less than the investment needed for a robot, but a robot gives a better ROI over the medium term.
In addition, prices will fall more as the technology becomes more widespread and affordable. For example, in 2010 the PR2 robot from the Willow Garage company cost 400,000 dollars, while in 2015 the Baxter robot from Rethink Robotics had a cost of 22,000 dollars.
The development of robotics applied to logistics in Europe and the United States would favor industries and keep jobs in these areas while reducing dependence on Asian technology, especially from Japan, China, and Korea.
→ Start now: how to create an automated supply chain
Types of robots and artificial intelligence in logistics
Automated arms and machinery
These are the robots that are the easiest to spot: arms that can pick up products, close and seal boxes, and move packages from one shelf to another.
This type of machinery has been the most used until now and it is not difficult to find it in many companies, specially from the automobile industry. What makes these robots different from conventional machinery is that they can tackle more complex tasks, apply analytics at the same time, and assist workers doing repetitive jobs like managing orders or arranging pallets.
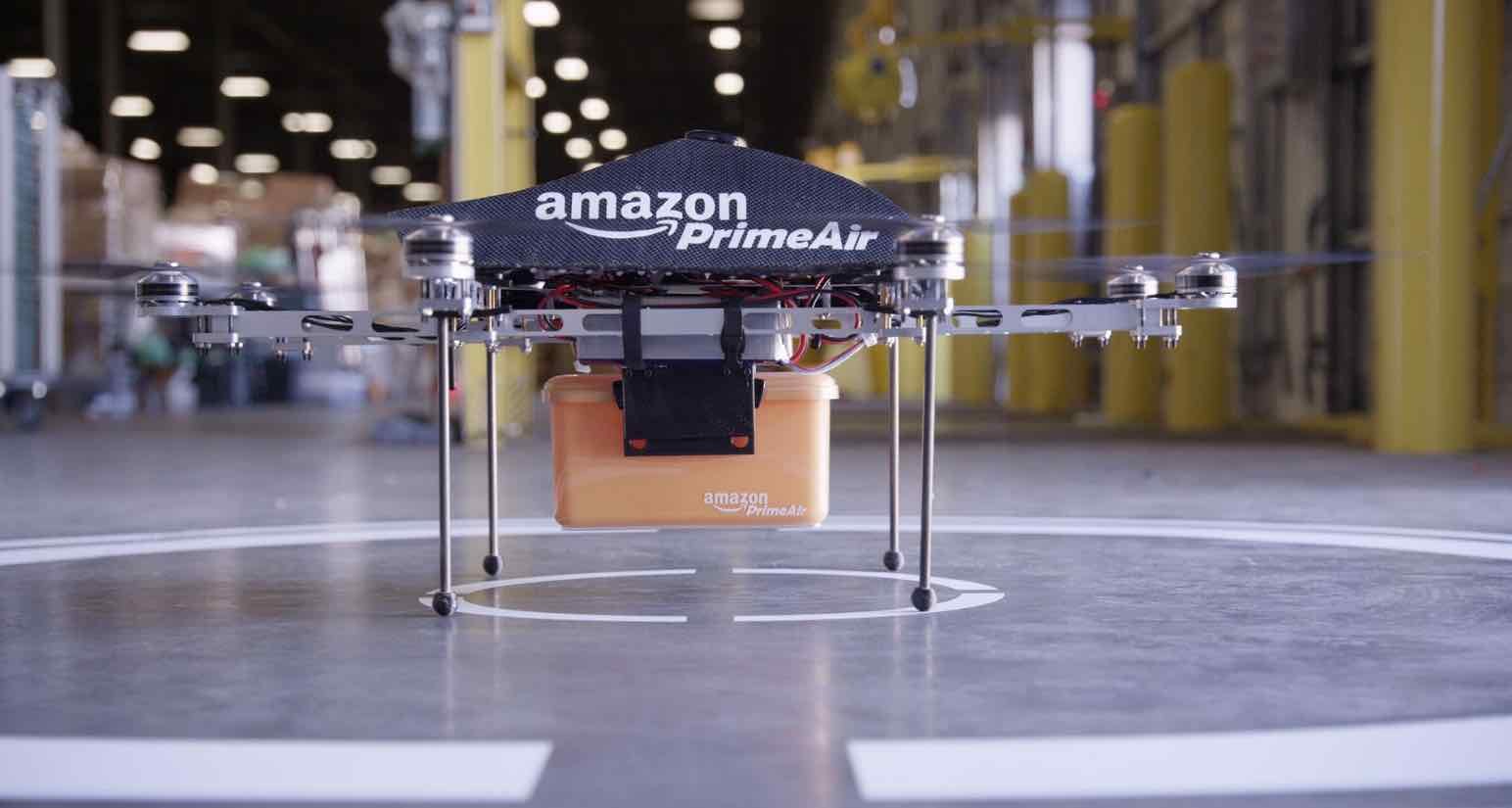
Drones
Drones are, without a doubt, the warehouse management robots that come to mind if we speak of the future and artificial intelligence.
A drone is a robot that can fly and carry a limited amount of weight, transport units, and reach difficult-to-access areas (this includes geographic areas, like isolated villages, and deep shelves or places that are higher in a warehouse).
There are different types of drones that can be more or less powerful depending on their antennas and battery for autonomous functioning.
RFID systems
Reading products with RFID tags is more complete than using a conventional barcode as RFID tags have more information. A drone with a RFID system can identify products in a warehouse and provide better control over locating and transferring units and inventory.
A drone with a RFID system can read thousands of labels in very little time when compared with a person doing the task manually. In addition, this information is immediately sent to the desired device, allowing for full control and connectivity between the robot and the manager.
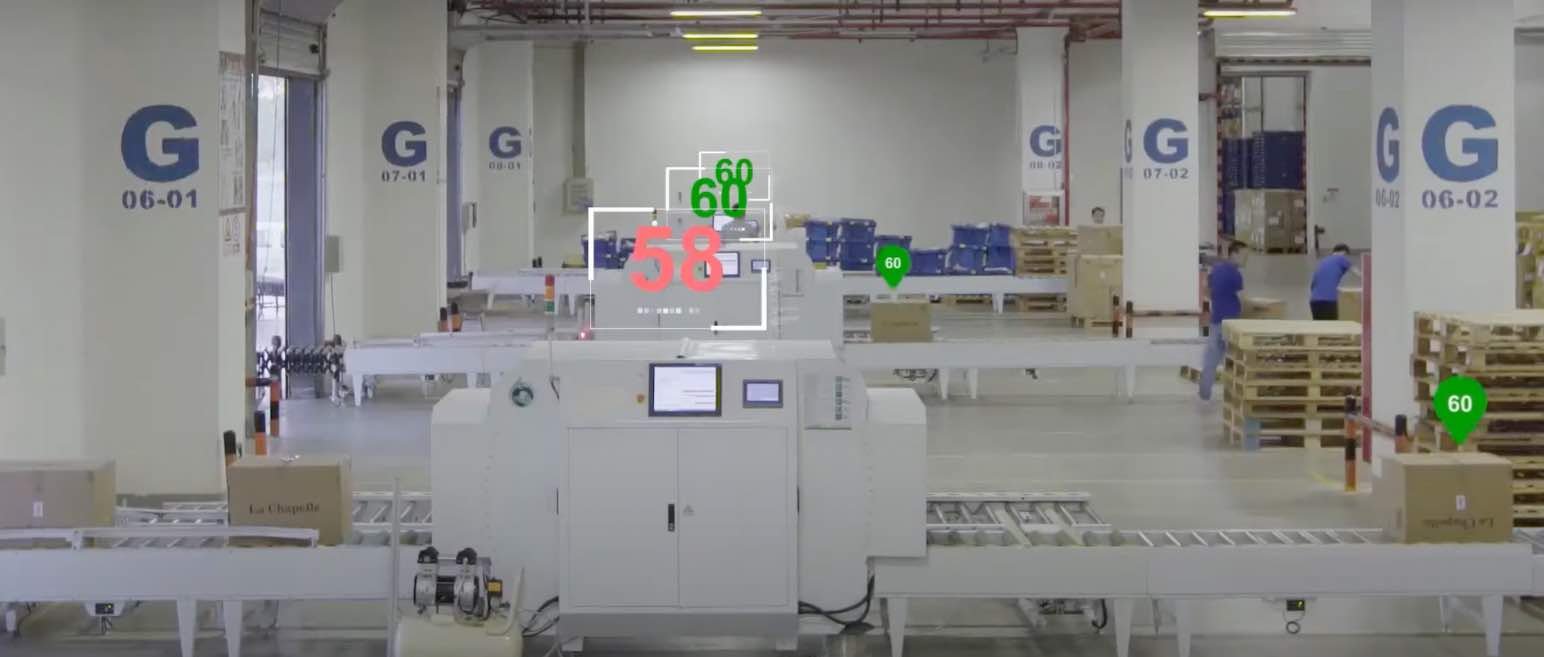
Another system that works using RFID tags automated arches. These are fixed structures, unlike drones. They can help to monitor a specific, high-traffic area like loading docks.
The arches have radiofrequency sensors that identify the merchandise and the direction it is going in (if it is incoming or outgoing from the warehouse), and they allow inventory data and order shipping data to be kept in real time.
While they are used in a fixed location, they normally include wheels so that they can be moved if necessary.
Robotic vehicles
Robotic vehicles are small, autonomous cars capable of moving about without a driver or remote control. They include systems to read QR codes and RFID signals so that they can follow paths in a warehouse while avoiding obstacles and identifying units and pallets.
Machine learning technology allows robotic vehicles to be independent and reliable, and they are usually a complement to the work of warehouse employees. That’s why they are known as cobots, or collaborative robots, as the employee tells them the transport or classification tasks that they must undertake automatically.
And, in this increasingly complex logistics structure another helping technological hand is PIM software (Product Information Management), which automates product information for an entire catalog and for the merchandise stored in a warehouse. A PIM solution is key to effective distribution, as it ensures that the product data is always correct by labeling and identifying products in orders and warehouses.
Advantages of robotics applied to distribution
- A reduction of logistics costs by between 20% and 40%, and an increase in productivity by between 25% and 70%, according to a study by Roland Berger that analyzes the impact of robotics on logistics until 2025.
- Automatic, fast identification of any item or pallet in a warehouse.
- Personalization of each robot’s configuration for different tasks and levels of complexity.
- Sound and light signals that complement the automatic warehouse work.
- Remote connections with devices from which you can view and monitor the robot’s work.
- More agile preparation of shipments and better precision in deliveries.
On the negative side, we can mention the impact that robotics can have on employment. It is estimated that up to 1.5 million logistics jobs can be lost in the Eurozone, which shows the importance of encouraging the learning of these new skills amongst human logistics teams and strengthening the industry itself to avoid the dominance of foreign technology.
→ You may be interested in: the future of autonomous cars in ecommerce
Uses of robotics in logistics
Management of warehouses and inventory
As we have already seen, automated robots with artificial intelligence are great allies in terms of managing the warehouse more safely and with better control.
Poor inventory management is one of the greatest distribution nightmares as it has a negative impact and implies losses for the company due to incorrect stock figures and shipping errors.

Drones and arches allow for logistics teams to have accurate and up-to-date inventory information in real time, which reduces the amount of time invested in repetitive review tasks, as well as errors, and costs. They also help to organize the warehouse, optimizing space and identifying empty areas.
These systems are especially important for companies with complex warehouses that have very dep or high shelves, or with a catalog with a lot of product variants that make it easier for employees to make mistakes.
→ More tips: how to achieve efficient inventory control
Inventory transfer
When goods are unloaded, moved, or selected for shipping, the tasks of picking and mobilization in logistics traditionally took a lot of time and involved safety risks for employees.
Robotics adds more safety and speed when unloading, lifting, storing, and packing any pallet – although not all drones and robots can handle the different weights and sizes.
In ecommerce, this option is quite useful as it allows the exact products of each order to be found in the warehouse, streamlining packing and shipping, and reorganizing shelves constantly.
→ Take note: how to create a distribution policy for your business
Order shipments
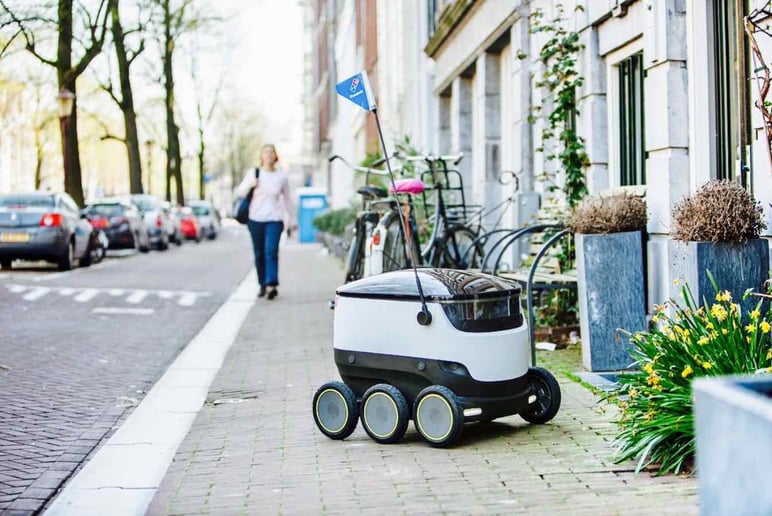
Up until now, we have been speaking of robotics and machinery in warehouses; however, there are also applications for outside the storage facility.
Autonomous vehicles and drones will also be more and more effective for shipping large goods or small orders for private customers, like in ecommerce. Remotely, a controller can review the signals sent by the vehicle, follow it in real time, and confirm customer satisfaction.
Currently, these robots work on the land or in the air, and they usually bring about a lot of headlines about their safety and efficiency. The majority of the companies that have included them as part of their logistics system use them only inside the warehouse. Outside of the warehouse, tests have been undertaken with small delivery robots by Amazon, UPS, and Domino’s Pizza.
These robots equipped with artificial intelligence could calculate the best route, cut down on costs as they work without fuel and without a driver, recognize obstacles, and adapt to different meteorological conditions like rain or snow. Nevertheless, we still must solve the question of their security when faced with external attacks and that of optimizing their costs; currently, this system is too expensive.
Conclusion
Robotics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning in logistics are not parts of a science fiction novel: they are the here and now which is beginning to materialize.
When faced with the technological changes that are just around the corner, it is key for the logistics industry to get support, knowledge, and financing assistance to adapt to the future which, little by little, is becoming more common. Training and preparation now will be the key to persist in the future without depending on cheap Asian technology and without seeing a negative impact on domestic jobs.
How to invest in high-tech logistics robotics is a big step. You can start by familiarizing yourself with the Sales Layer PIM automated catalog management system for free for 30 days and, thus, unleash all the advantages of automation which is already within the reach of any company.








.png?width=520&name=Blog%20Partner%20(1).png)
